| diagram | 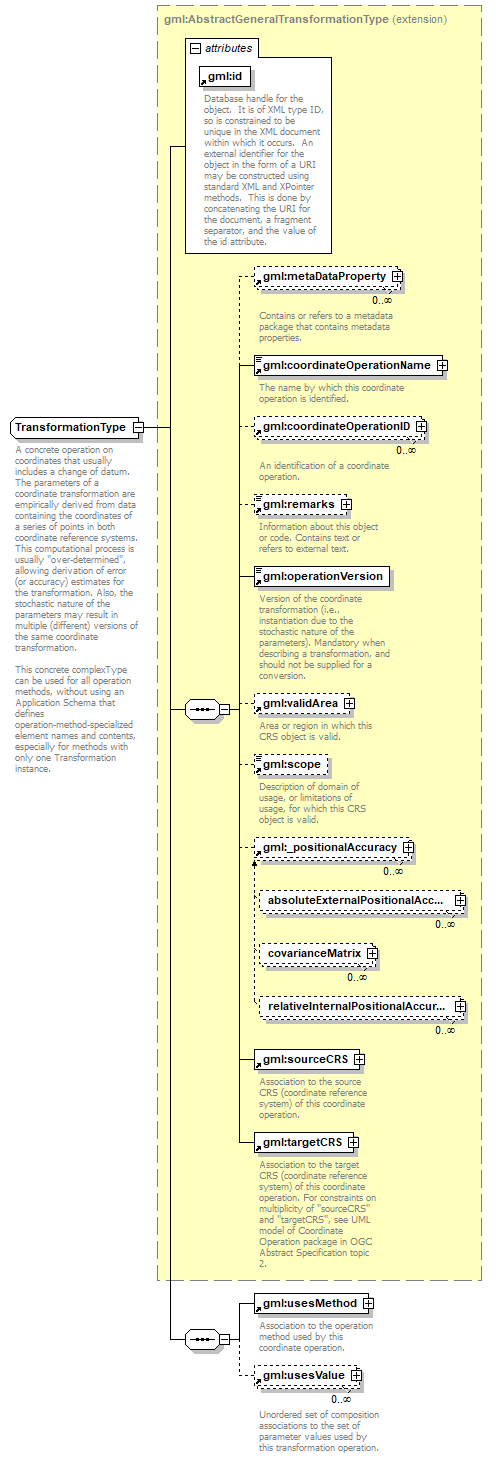 |
||||||||||||||
| namespace | http://www.opengis.net/gml | ||||||||||||||
| type | extension of gml:AbstractGeneralTransformationType | ||||||||||||||
| properties |
|
||||||||||||||
| children | gml:metaDataProperty gml:coordinateOperationName gml:coordinateOperationID gml:remarks gml:operationVersion gml:validArea gml:scope gml:_positionalAccuracy gml:sourceCRS gml:targetCRS gml:usesMethod gml:usesValue | ||||||||||||||
| used by |
|
||||||||||||||
| attributes |
|
||||||||||||||
| annotation |
|
||||||||||||||
| source | <xs:complexType name="TransformationType"> <xs:annotation> <xs:documentation>A concrete operation on coordinates that usually includes a change of datum. The parameters of a coordinate transformation are empirically derived from data containing the coordinates of a series of points in both coordinate reference systems. This computational process is usually "over-determined", allowing derivation of error (or accuracy) estimates for the transformation. Also, the stochastic nature of the parameters may result in multiple (different) versions of the same coordinate transformation. This concrete complexType can be used for all operation methods, without using an Application Schema that defines operation-method-specialized element names and contents, especially for methods with only one Transformation instance. </xs:documentation> </xs:annotation> <xs:complexContent> <xs:extension base="gml:AbstractGeneralTransformationType"> <xs:sequence> <xs:element ref="gml:usesMethod"/> <xs:element ref="gml:usesValue" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"> <xs:annotation> <xs:documentation>Unordered set of composition associations to the set of parameter values used by this transformation operation. </xs:documentation> </xs:annotation> </xs:element> </xs:sequence> </xs:extension> </xs:complexContent> </xs:complexType> |
XML Schema documentation generated by XMLSpy Schema Editor http://www.altova.com/xmlspy