| diagram | 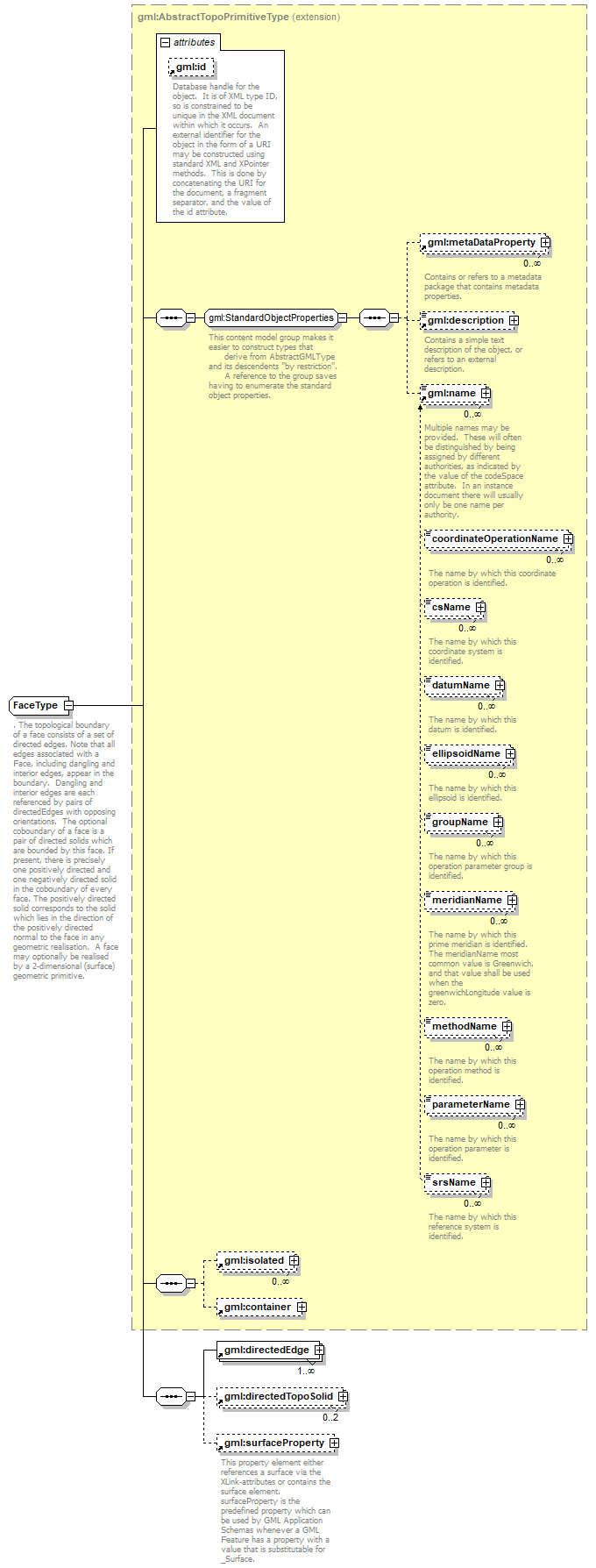 |
||||||||||||||
| namespace | http://www.opengis.net/gml | ||||||||||||||
| type | extension of gml:AbstractTopoPrimitiveType | ||||||||||||||
| properties |
|
||||||||||||||
| children | gml:metaDataProperty gml:description gml:name gml:isolated gml:container gml:directedEdge gml:directedTopoSolid gml:surfaceProperty | ||||||||||||||
| used by |
|
||||||||||||||
| attributes |
|
||||||||||||||
| annotation |
|
||||||||||||||
| source | <xs:complexType name="FaceType"> <xs:annotation> <xs:documentation>. The topological boundary of a face consists of a set of directed edges. Note that all edges associated with a Face, including dangling and interior edges, appear in the boundary. Dangling and interior edges are each referenced by pairs of directedEdges with opposing orientations. The optional coboundary of a face is a pair of directed solids which are bounded by this face. If present, there is precisely one positively directed and one negatively directed solid in the coboundary of every face. The positively directed solid corresponds to the solid which lies in the direction of the positively directed normal to the face in any geometric realisation. A face may optionally be realised by a 2-dimensional (surface) geometric primitive.</xs:documentation> </xs:annotation> <xs:complexContent> <xs:extension base="gml:AbstractTopoPrimitiveType"> <xs:sequence> <xs:element ref="gml:directedEdge" maxOccurs="unbounded"/> <xs:element ref="gml:directedTopoSolid" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="2"/> <xs:element ref="gml:surfaceProperty" minOccurs="0"/> </xs:sequence> </xs:extension> </xs:complexContent> </xs:complexType> |
XML Schema documentation generated by XMLSpy Schema Editor http://www.altova.com/xmlspy