| diagram | 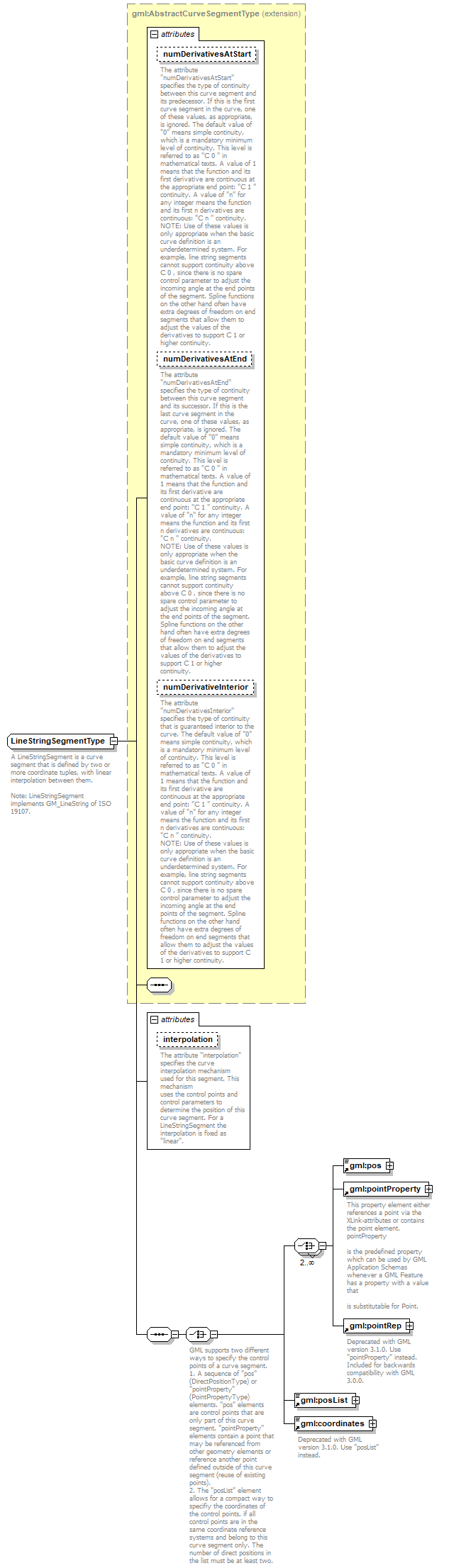 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| namespace | http://www.opengis.net/gml | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| type | extension of gml:AbstractCurveSegmentType | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| children | gml:pos gml:pointProperty gml:pointRep gml:posList gml:coordinates | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| used by |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| attributes |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| annotation |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| source | <xs:complexType name="LineStringSegmentType"> <xs:annotation> <xs:documentation>A LineStringSegment is a curve segment that is defined by two or more coordinate tuples, with linear interpolation between them. Note: LineStringSegment implements GM_LineString of ISO 19107.</xs:documentation> </xs:annotation> <xs:complexContent> <xs:extension base="gml:AbstractCurveSegmentType"> <xs:sequence> <xs:choice> <xs:annotation> <xs:documentation>GML supports two different ways to specify the control points of a curve segment. 1. A sequence of "pos" (DirectPositionType) or "pointProperty" (PointPropertyType) elements. "pos" elements are control points that are only part of this curve segment, "pointProperty" elements contain a point that may be referenced from other geometry elements or reference another point defined outside of this curve segment (reuse of existing points). 2. The "posList" element allows for a compact way to specifiy the coordinates of the control points, if all control points are in the same coordinate reference systems and belong to this curve segment only. The number of direct positions in the list must be at least two.</xs:documentation> </xs:annotation> <xs:choice minOccurs="2" maxOccurs="unbounded"> <xs:element ref="gml:pos"/> <xs:element ref="gml:pointProperty"/> <xs:element ref="gml:pointRep"> <xs:annotation> <xs:documentation>Deprecated with GML version 3.1.0. Use "pointProperty" instead. Included for backwards compatibility with GML 3.0.0.</xs:documentation> </xs:annotation> </xs:element> </xs:choice> <xs:element ref="gml:posList"/> <xs:element ref="gml:coordinates"> <xs:annotation> <xs:documentation>Deprecated with GML version 3.1.0. Use "posList" instead.</xs:documentation> </xs:annotation> </xs:element> </xs:choice> </xs:sequence> <xs:attribute name="interpolation" type="gml:CurveInterpolationType" fixed="linear"> <xs:annotation> <xs:documentation>The attribute "interpolation" specifies the curve interpolation mechanism used for this segment. This mechanism uses the control points and control parameters to determine the position of this curve segment. For a LineStringSegment the interpolation is fixed as "linear".</xs:documentation> </xs:annotation> </xs:attribute> </xs:extension> </xs:complexContent> </xs:complexType> |
attribute LineStringSegmentType/@interpolation
| type | gml:CurveInterpolationType | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| facets |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| annotation |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| source | <xs:attribute name="interpolation" type="gml:CurveInterpolationType" fixed="linear"> <xs:annotation> <xs:documentation>The attribute "interpolation" specifies the curve interpolation mechanism used for this segment. This mechanism uses the control points and control parameters to determine the position of this curve segment. For a LineStringSegment the interpolation is fixed as "linear".</xs:documentation> </xs:annotation> </xs:attribute> |
XML Schema documentation generated by XMLSpy Schema Editor http://www.altova.com/xmlspy