| diagram | 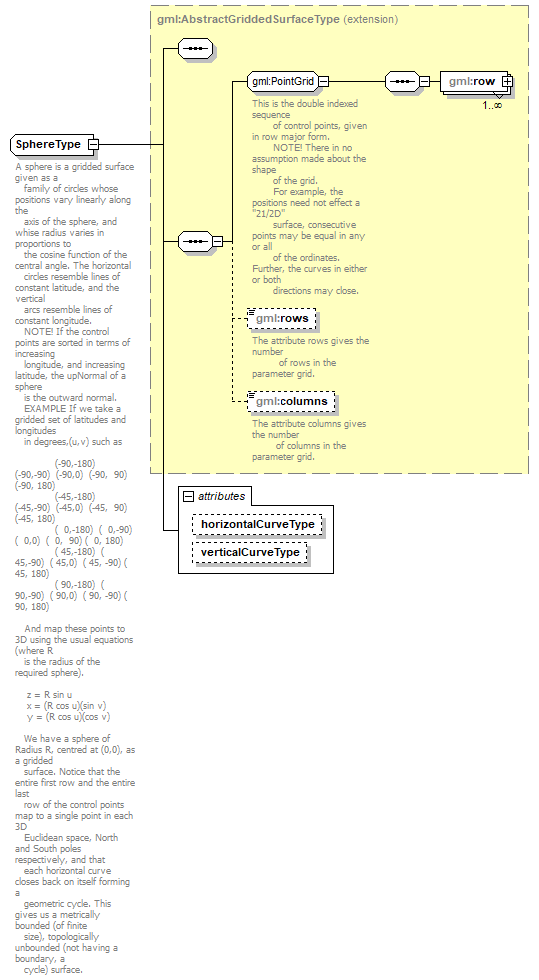 |
||||||||||||||||||
| namespace | http://www.opengis.net/gml | ||||||||||||||||||
| type | extension of gml:AbstractGriddedSurfaceType | ||||||||||||||||||
| properties |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| children | gml:row gml:rows gml:columns | ||||||||||||||||||
| used by |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| attributes |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| annotation |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| source | <xs:complexType name="SphereType"> <xs:annotation> <xs:documentation>A sphere is a gridded surface given as a family of circles whose positions vary linearly along the axis of the sphere, and whise radius varies in proportions to the cosine function of the central angle. The horizontal circles resemble lines of constant latitude, and the vertical arcs resemble lines of constant longitude. NOTE! If the control points are sorted in terms of increasing longitude, and increasing latitude, the upNormal of a sphere is the outward normal. EXAMPLE If we take a gridded set of latitudes and longitudes in degrees,(u,v) such as (-90,-180) (-90,-90) (-90,0) (-90, 90) (-90, 180) (-45,-180) (-45,-90) (-45,0) (-45, 90) (-45, 180) ( 0,-180) ( 0,-90) ( 0,0) ( 0, 90) ( 0, 180) ( 45,-180) ( 45,-90) ( 45,0) ( 45, -90) ( 45, 180) ( 90,-180) ( 90,-90) ( 90,0) ( 90, -90) ( 90, 180) And map these points to 3D using the usual equations (where R is the radius of the required sphere). z = R sin u x = (R cos u)(sin v) y = (R cos u)(cos v) We have a sphere of Radius R, centred at (0,0), as a gridded surface. Notice that the entire first row and the entire last row of the control points map to a single point in each 3D Euclidean space, North and South poles respectively, and that each horizontal curve closes back on itself forming a geometric cycle. This gives us a metrically bounded (of finite size), topologically unbounded (not having a boundary, a cycle) surface.</xs:documentation> </xs:annotation> <xs:complexContent> <xs:extension base="gml:AbstractGriddedSurfaceType"> <xs:attribute name="horizontalCurveType" type="gml:CurveInterpolationType" fixed="circularArc3Points"/> <xs:attribute name="verticalCurveType" type="gml:CurveInterpolationType" fixed="circularArc3Points"/> </xs:extension> </xs:complexContent> </xs:complexType> |
attribute SphereType/@horizontalCurveType
| type | gml:CurveInterpolationType | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| facets |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| source | <xs:attribute name="horizontalCurveType" type="gml:CurveInterpolationType" fixed="circularArc3Points"/> |
attribute SphereType/@verticalCurveType
| type | gml:CurveInterpolationType | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| properties |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| facets |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| source | <xs:attribute name="verticalCurveType" type="gml:CurveInterpolationType" fixed="circularArc3Points"/> |
XML Schema documentation generated by XMLSpy Schema Editor http://www.altova.com/xmlspy