| diagram |
 |
| namespace |
http://www.opengis.net/gml |
| type |
extension of gml:AbstractCurveSegmentType |
| properties |
| base | gml:AbstractCurveSegmentType |
|
| children |
gml:offsetBase gml:distance gml:refDirection |
| used by |
|
| attributes |
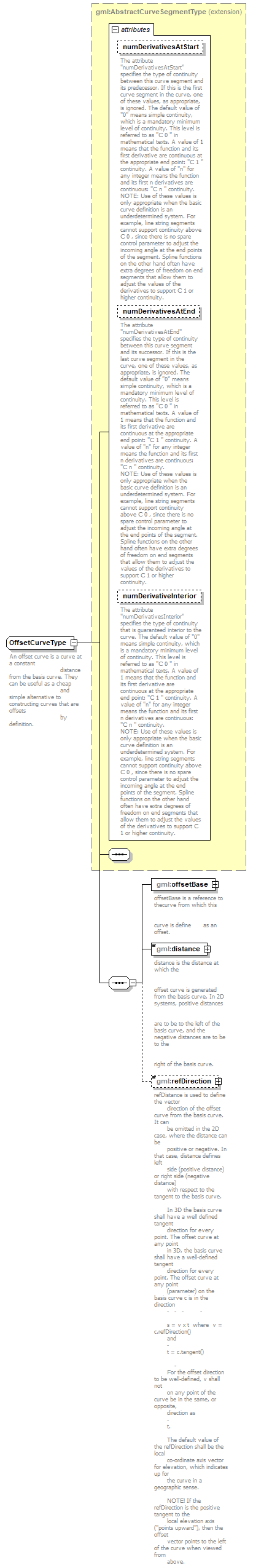
| Name | Type | Use | Default | Fixed | annotation | | numDerivativesAtStart | xs:integer | optional | 0 | | | documentation | The attribute "numDerivativesAtStart" specifies the type of continuity between this curve segment and its predecessor. If this is the first curve segment in the curve, one of these values, as appropriate, is ignored. The default value of "0" means simple continuity, which is a mandatory minimum level of continuity. This level is referred to as "C 0 " in mathematical texts. A value of 1 means that the function and its first derivative are continuous at the appropriate end point: "C 1 " continuity. A value of "n" for any integer means the function and its first n derivatives are continuous: "C n " continuity.
NOTE: Use of these values is only appropriate when the basic curve definition is an underdetermined system. For example, line string segments cannot support continuity above C 0 , since there is no spare control parameter to adjust the incoming angle at the end points of the segment. Spline functions on the other hand often have extra degrees of freedom on end segments that allow them to adjust the values of the derivatives to support C 1 or higher continuity. |
| | numDerivativesAtEnd | xs:integer | optional | 0 | | | documentation | The attribute "numDerivativesAtEnd" specifies the type of continuity between this curve segment and its successor. If this is the last curve segment in the curve, one of these values, as appropriate, is ignored. The default value of "0" means simple continuity, which is a mandatory minimum level of continuity. This level is referred to as "C 0 " in mathematical texts. A value of 1 means that the function and its first derivative are continuous at the appropriate end point: "C 1 " continuity. A value of "n" for any integer means the function and its first n derivatives are continuous: "C n " continuity.
NOTE: Use of these values is only appropriate when the basic curve definition is an underdetermined system. For example, line string segments cannot support continuity above C 0 , since there is no spare control parameter to adjust the incoming angle at the end points of the segment. Spline functions on the other hand often have extra degrees of freedom on end segments that allow them to adjust the values of the derivatives to support C 1 or higher continuity. |
| | numDerivativeInterior | xs:integer | optional | 0 | | | documentation | The attribute "numDerivativesInterior" specifies the type of continuity that is guaranteed interior to the curve. The default value of "0" means simple continuity, which is a mandatory minimum level of continuity. This level is referred to as "C 0 " in mathematical texts. A value of 1 means that the function and its first derivative are continuous at the appropriate end point: "C 1 " continuity. A value of "n" for any integer means the function and its first n derivatives are continuous: "C n " continuity.
NOTE: Use of these values is only appropriate when the basic curve definition is an underdetermined system. For example, line string segments cannot support continuity above C 0 , since there is no spare control parameter to adjust the incoming angle at the end points of the segment. Spline functions on the other hand often have extra degrees of freedom on end segments that allow them to adjust the values of the derivatives to support C 1 or higher continuity. |
|
|
| annotation |
| documentation | An offset curve is a curve at a constant
distance from the basis curve. They can be useful as a cheap
and simple alternative to constructing curves that are offsets
by definition. |
|
| source |
<xs:complexType name="OffsetCurveType">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>An offset curve is a curve at a constant
distance from the basis curve. They can be useful as a cheap
and simple alternative to constructing curves that are offsets
by definition.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
<xs:complexContent>
<xs:extension base="gml:AbstractCurveSegmentType">
<xs:sequence>
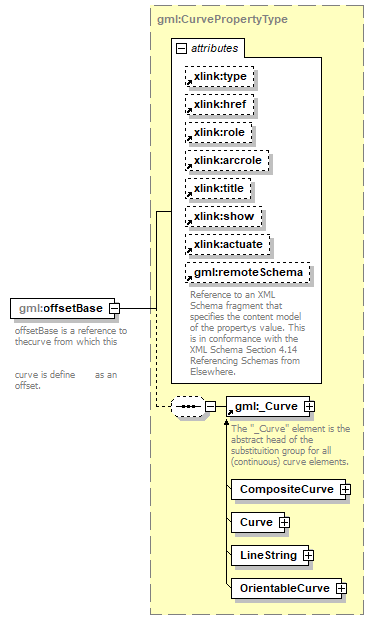
<xs:element name="offsetBase" type="gml:CurvePropertyType">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>offsetBase is a reference to thecurve from which this
curve is define as an offset.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
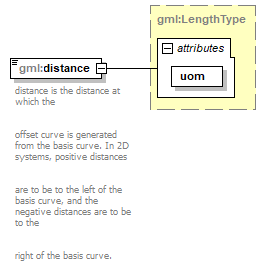
<xs:element name="distance" type="gml:LengthType">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>distance is the distance at which the
offset curve is generated from the basis curve. In 2D systems, positive distances
are to be to the left of the basis curve, and the negative distances are to be to the
right of the basis curve.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="refDirection" type="gml:VectorType" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>refDistance is used to define the vector
direction of the offset curve from the basis curve. It can
be omitted in the 2D case, where the distance can be
positive or negative. In that case, distance defines left
side (positive distance) or right side (negative distance)
with respect to the tangent to the basis curve.
In 3D the basis curve shall have a well defined tangent
direction for every point. The offset curve at any point
in 3D, the basis curve shall have a well-defined tangent
direction for every point. The offset curve at any point
(parameter) on the basis curve c is in the direction
- - - -
s = v x t where v = c.refDirection()
and
-
t = c.tangent()
-
For the offset direction to be well-defined, v shall not
on any point of the curve be in the same, or opposite,
direction as
-
t.
The default value of the refDirection shall be the local
co-ordinate axis vector for elevation, which indicates up for
the curve in a geographic sense.
NOTE! If the refDirection is the positive tangent to the
local elevation axis ("points upward"), then the offset
vector points to the left of the curve when viewed from
above.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:extension>
</xs:complexContent>
</xs:complexType> |
| diagram |
 |
| namespace |
http://www.opengis.net/gml |
| type |
gml:VectorType |
| properties |
| isRef | 0 | | minOcc | 0 | | maxOcc | 1 | | content | complex |
|
| attributes |
| Name | Type | Use | Default | Fixed | annotation | | srsName | xs:anyURI | optional | | | | documentation | In general this reference points to a CRS instance of gml:CoordinateReferenceSystemType
(see coordinateReferenceSystems.xsd). For well known references it is not required that the CRS description exists at the
location the URI points to. If no srsName attribute is given, the CRS must be specified as part of the larger context this
geometry element is part of, e.g. a geometric element like point, curve, etc. It is expected that this attribute will be specified
at the direct position level only in rare cases. |
| | srsDimension | xs:positiveInteger | optional | | | | documentation | The "srsDimension" is the length of coordinate sequence (the number of entries in the list). This dimension is
specified by the coordinate reference system. When the srsName attribute is omitted, this attribute shall be omitted. |
| | axisLabels | gml:NCNameList | optional | | | | documentation | Ordered list of labels for all the axes of this CRS. The gml:axisAbbrev value should be used for these axis
labels, after spaces and forbiddden characters are removed. When the srsName attribute is included, this attribute is optional.
When the srsName attribute is omitted, this attribute shall also be omitted. |
| | uomLabels | gml:NCNameList | optional | | | | documentation | Ordered list of unit of measure (uom) labels for all the axes of this CRS. The value of the string in the
gml:catalogSymbol should be used for this uom labels, after spaces and forbiddden characters are removed. When the
axisLabels attribute is included, this attribute shall also be included. When the axisLabels attribute is omitted, this attribute
shall also be omitted. |
|
|
| annotation |
| documentation | refDistance is used to define the vector
direction of the offset curve from the basis curve. It can
be omitted in the 2D case, where the distance can be
positive or negative. In that case, distance defines left
side (positive distance) or right side (negative distance)
with respect to the tangent to the basis curve.
In 3D the basis curve shall have a well defined tangent
direction for every point. The offset curve at any point
in 3D, the basis curve shall have a well-defined tangent
direction for every point. The offset curve at any point
(parameter) on the basis curve c is in the direction
- - - -
s = v x t where v = c.refDirection()
and
-
t = c.tangent()
-
For the offset direction to be well-defined, v shall not
on any point of the curve be in the same, or opposite,
direction as
-
t.
The default value of the refDirection shall be the local
co-ordinate axis vector for elevation, which indicates up for
the curve in a geographic sense.
NOTE! If the refDirection is the positive tangent to the
local elevation axis ("points upward"), then the offset
vector points to the left of the curve when viewed from
above. |
|
| source |
<xs:element name="refDirection" type="gml:VectorType" minOccurs="0">
<xs:annotation>
<xs:documentation>refDistance is used to define the vector
direction of the offset curve from the basis curve. It can
be omitted in the 2D case, where the distance can be
positive or negative. In that case, distance defines left
side (positive distance) or right side (negative distance)
with respect to the tangent to the basis curve.
In 3D the basis curve shall have a well defined tangent
direction for every point. The offset curve at any point
in 3D, the basis curve shall have a well-defined tangent
direction for every point. The offset curve at any point
(parameter) on the basis curve c is in the direction
- - - -
s = v x t where v = c.refDirection()
and
-
t = c.tangent()
-
For the offset direction to be well-defined, v shall not
on any point of the curve be in the same, or opposite,
direction as
-
t.
The default value of the refDirection shall be the local
co-ordinate axis vector for elevation, which indicates up for
the curve in a geographic sense.
NOTE! If the refDirection is the positive tangent to the
local elevation axis ("points upward"), then the offset
vector points to the left of the curve when viewed from
above.</xs:documentation>
</xs:annotation>
</xs:element> |